.png)
.png)
.png)

_1766125289_WNo_1600d900.webp)
In the world of welding and fabrication, efficiency, precision, and safety are paramount. If you're a welding professional, manufacturing engineer, shop owner, or buyer researching equipment to optimize your operations, you've likely come across the term "welding positioner." But what is a welding positioner exactly? At its core, a welding positioner is a specialized mechanical device designed to hold, rotate, and manipulate workpieces during the welding process. This allows welders to position materials at the most optimal angles, ensuring consistent, high-quality welds without the need for constant manual repositioning.
Welding positioners come in various forms, from simple manual setups to advanced automated systems, and they play a crucial role in industries like manufacturing, shipbuilding, construction, and fabrication. By enabling welders to work on flat or horizontal surfaces more easily, these tools reduce physical strain, minimize errors, and boost overall productivity. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore everything you need to know about welding positioners, including how they work, their types, benefits, applications, safety considerations, and more. Whether you're evaluating options for your shop or looking to enhance your welding processes, understanding welding positioners can help you make informed decisions.
As a leader in welding equipment solutions, MISA Welding offers a range of high-quality welding positioners tailored to meet diverse industrial needs.
Understanding how welding positioners work is essential for appreciating their value in modern fabrication shops. At a basic level, a welding positioner consists of a sturdy base, a rotatable table or fixture, and a drive system (manual, motorized, or automated) that allows precise control over the workpiece's orientation.
The process typically unfolds as follows:
Advanced positioners integrate with robotic arms or CNC controls for fully automated welding, synchronizing rotation with torch movement for complex, multi-pass welds.
This mechanism transforms challenging overhead or vertical welds into manageable downhand welds, significantly improving penetration, bead appearance, and overall structural integrity.
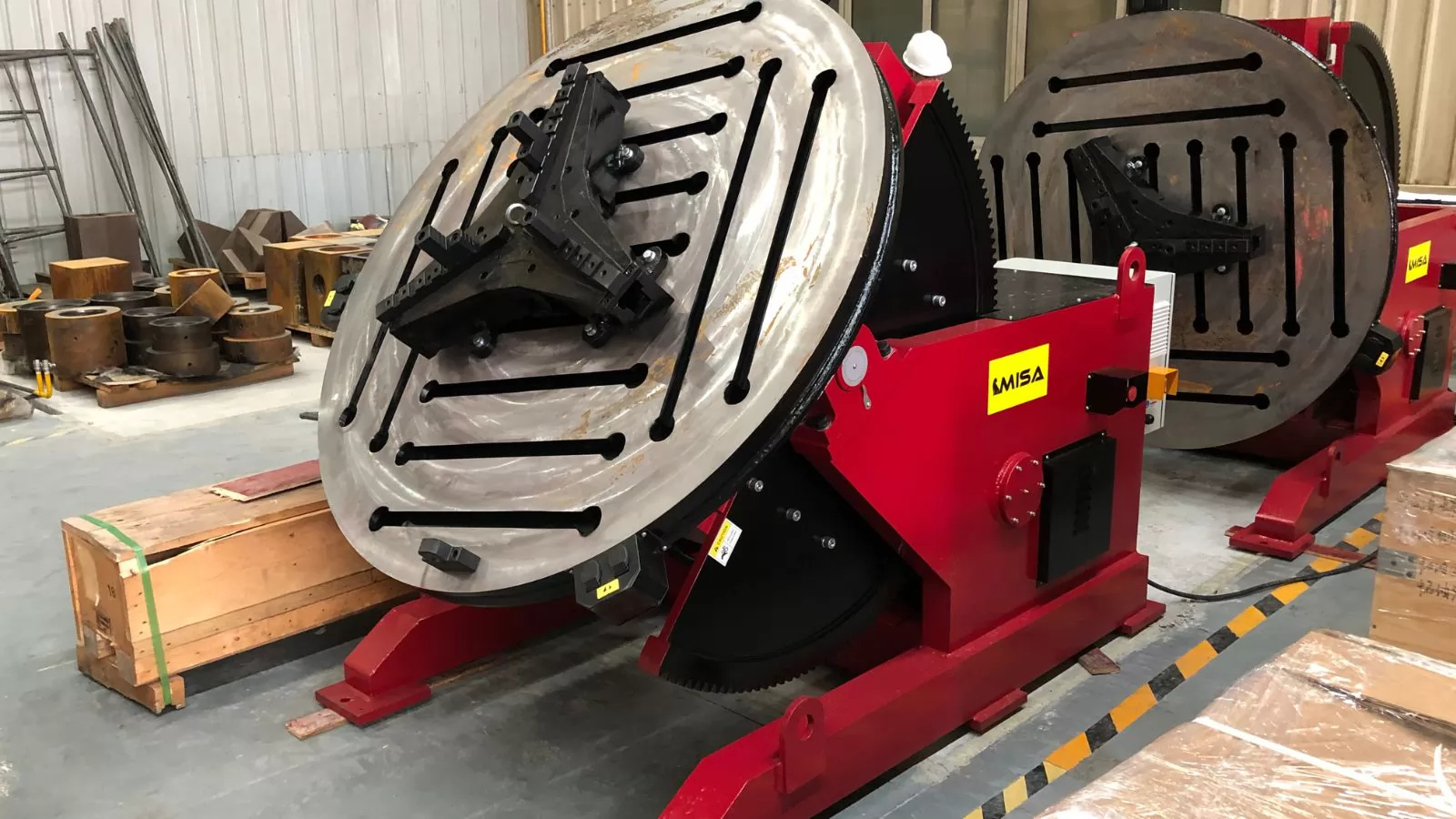
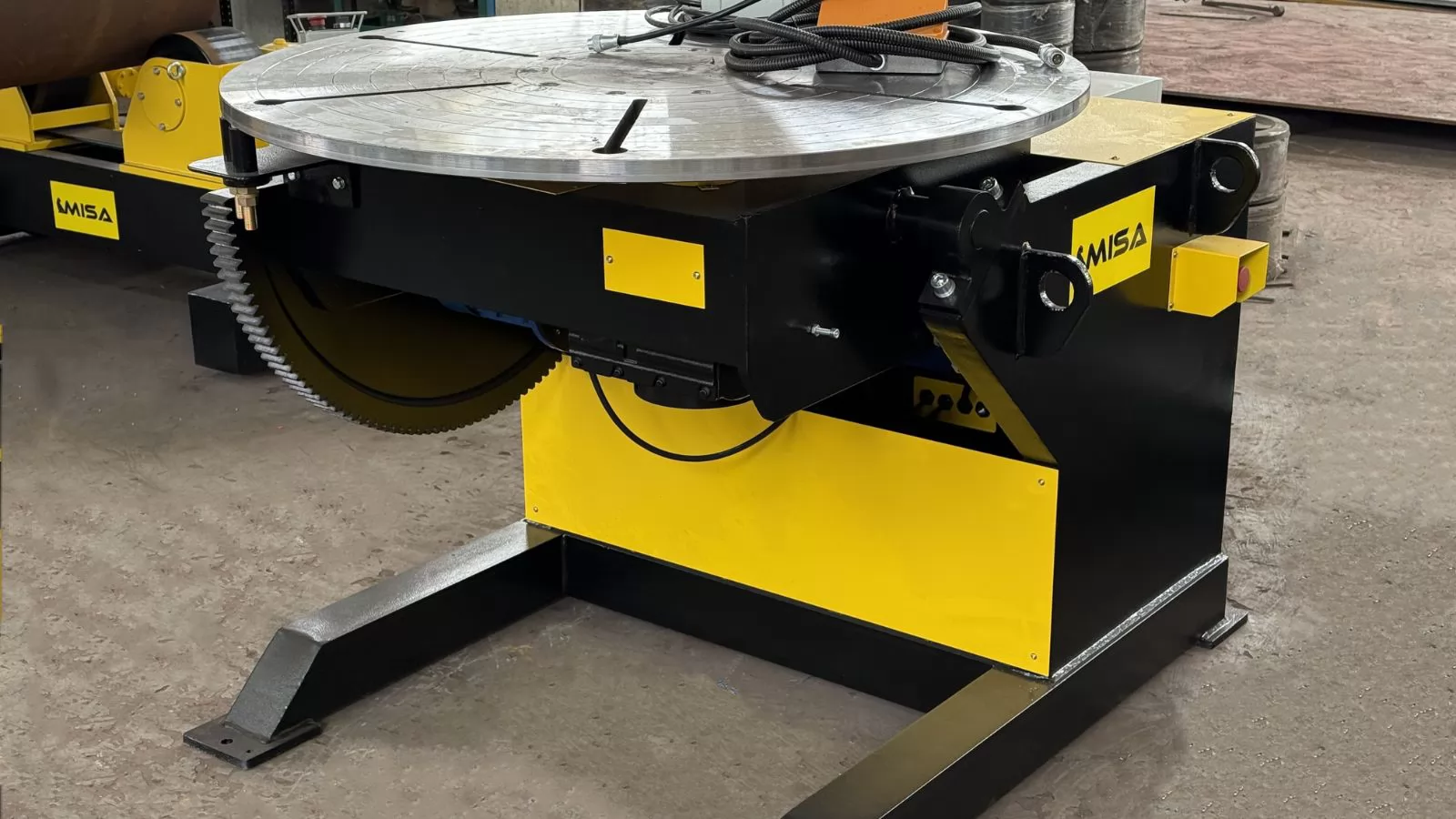
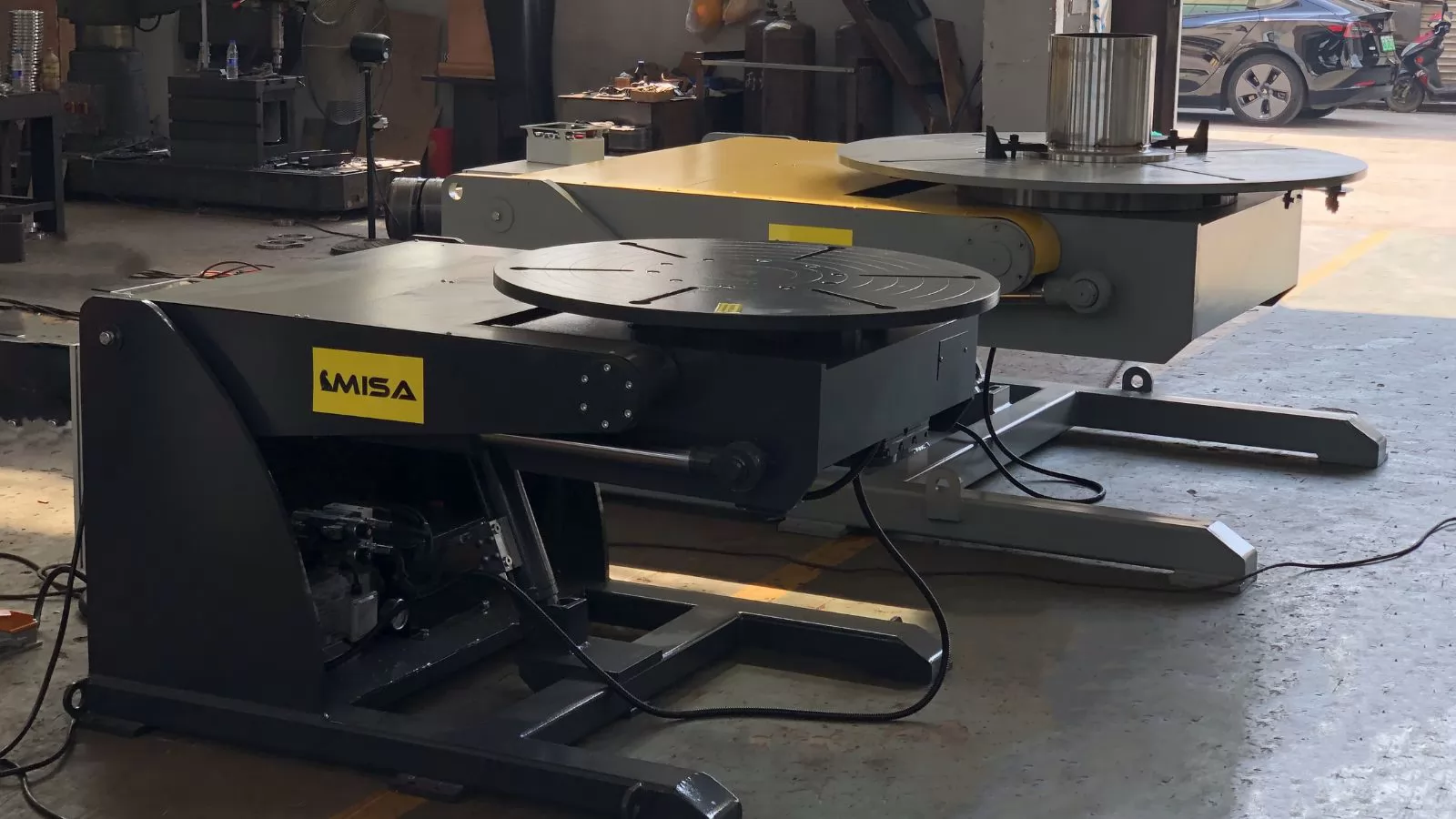



When researching what is a welding positioner, one of the most important aspects to understand is the variety of welding positioner types available. These machines are engineered to meet different project sizes, workpiece geometries, production volumes, and budget requirements.
While there are numerous configurations, the most common categories include:
Each type offers specific advantages depending on the workpiece size, weight, and welding process. Choosing the right type ensures maximum efficiency and weld quality.
For a detailed breakdown of all major welding positioner types, including specifications, capacities, and real-world examples, we recommend reading our in-depth resource:
Suggested internal link: What Are the Different Types of Welding Positioners?
Investing in a welding positioner can transform your shop’s productivity, weld quality, and worker safety. Here are the key welding positioner benefits that make these machines indispensable for serious fabricators, manufacturers, and repair shops:
By allowing the welder to maintain a consistent torch angle and travel speed, positioners produce smoother, more uniform welds with better penetration and fewer defects. Gravity-assisted downhand welding reduces porosity, undercutting, and spatter compared to manual overhead or vertical welding.
Rotating the workpiece eliminates the need for constant repositioning, reducing downtime between welds. Automated or variable-speed models can run continuously, supporting high-volume production.
Welders no longer have to climb ladders, work in awkward positions, or hold heavy pieces for long periods. This reduces physical strain and lowers the risk of repetitive stress injuries.
Controlled rotation and stable fixturing minimize the chance of workpiece movement or tipping. Welders can stay in safer, more comfortable positions, reducing exposure to harmful fumes and arc radiation.
Higher first-pass success rates mean less rework and material waste. Faster cycle times also lower labor costs and increase throughput, delivering a strong ROI.
Modern positioners can handle a wide range of workpiece sizes, shapes, and weights—from small fittings to massive tanks and pressure vessels.
In short, a welding positioner is not just a convenience; it’s a strategic tool that elevates the entire welding operation.
Suggested link: Discover the full range of MISA Welding positioners built for durability and precision.
Positioners excel at welding circumferential seams on pipes, elbows, flanges, and pressure vessels. They ensure consistent weld quality on round parts, making them a staple in oil & gas, chemical processing, and power generation.
Large cylindrical tanks, silos, and hoppers require multiple welds around the circumference. Headstock & tailstock positioners support and rotate these heavy components safely and accurately.
Fabrication of rollers, gears, drums, and structural components for mining, construction, and agricultural equipment often relies on positioners to handle large, awkward assemblies.
Precision welding of turbine components, landing gear, and structural frames benefits from the controlled rotation and repeatability of automated positioners.
Welding of hull sections, propeller shafts, and piping systems on ships and platforms uses large-scale positioners to maintain alignment and quality under demanding conditions.
Exhaust systems, fuel tanks, and chassis components are frequently welded using turntable or benchtop positioners for high-volume production.
Smaller, portable positioners are ideal for rebuilding valves, pump housings, and worn machinery parts.
No matter the industry, welding positioners help fabricators achieve higher-quality welds faster and with less effort.
Suggested link: Browse MISA Welding’s industry-specific solutions for pipe, tank, and heavy fabrication.
Safety should always be a top priority when operating welding equipment, and welding positioner safety is no exception. These machines involve moving parts, heavy loads, and integration with high-heat welding processes, so proper protocols are essential to prevent accidents, injuries, and equipment damage. Below, we outline key safety considerations for users, from setup to ongoing maintenance.
Ensure the positioner is mounted on a stable, level surface capable of supporting its maximum load rating. Use anchor bolts if necessary to prevent tipping. Always balance the workpiece around the center of rotation to avoid uneven forces that could cause instability or failure.
Never exceed the manufacturer's specified weight and torque limits. Overloading can lead to mechanical failure, such as gear stripping or motor burnout, potentially causing the workpiece to fall.
All users should receive thorough training on the specific model, including controls, emergency stops, and lockout/tagout procedures. Familiarity with speed settings and rotation directions is crucial to avoid pinch points or entanglement hazards.
Welders must wear appropriate PPE, including welding helmets, gloves, flame-resistant clothing, and safety glasses. Positioners reduce ergonomic risks but don't eliminate exposure to arc flash, sparks, or fumes—use ventilation systems or respirators as needed.
Look for positioners with built-in safety interlocks, such as automatic stops if overload is detected, or foot pedals for hands-free control. Always test emergency brakes before use.
Regularly inspect for wear on bearings, drives, and electrical components. Lubricate moving parts per the manual and check for loose fixtures. Schedule professional servicing to maintain compliance with standards like OSHA or ANSI.
When pairing with robotic arms or manipulators, ensure synchronized safety protocols to prevent collisions. Use guarding around pinch points and keep bystanders at a safe distance.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can minimize risks and create a safer welding environment. Remember, consulting the equipment manual and local regulations is vital for compliance.
When searching for the best welding positioners, focus on these key factors:
Reputable manufacturers like MISA Welding offer customizable options to match your exact needs, from compact benchtop models to heavy-duty industrial systems.
Q: What is the main purpose of a welding positioner?
A: To hold and rotate the workpiece so the welder can work in the optimal flat or horizontal position, improving weld quality and productivity.
Q: Can a welding positioner be used with robotic welding?
A: Yes—many modern positioners are designed for robotic integration, offering precise synchronization for automated welding.
Q: How much does a welding positioner cost?
A: Prices vary widely based on capacity, features, and customization. Contact a supplier like MISA Welding for a quote tailored to your requirements.
A welding positioner is a game-changing tool that delivers superior weld quality, higher productivity, better ergonomics, and enhanced safety. Whether you’re fabricating pipe, building tanks, or running high-volume production, the right positioner can significantly elevate your shop’s performance.
At MISA Welding, we specialize in building durable, high-performance welding positioners tailored to your specific applications. Ready to improve your welding process?
Explore MISA Welding’s complete line of welding positioners today and discover the perfect solution for your shop. Contact our team for expert advice, custom configurations, and competitive pricing.