.png)
.png)
.png)
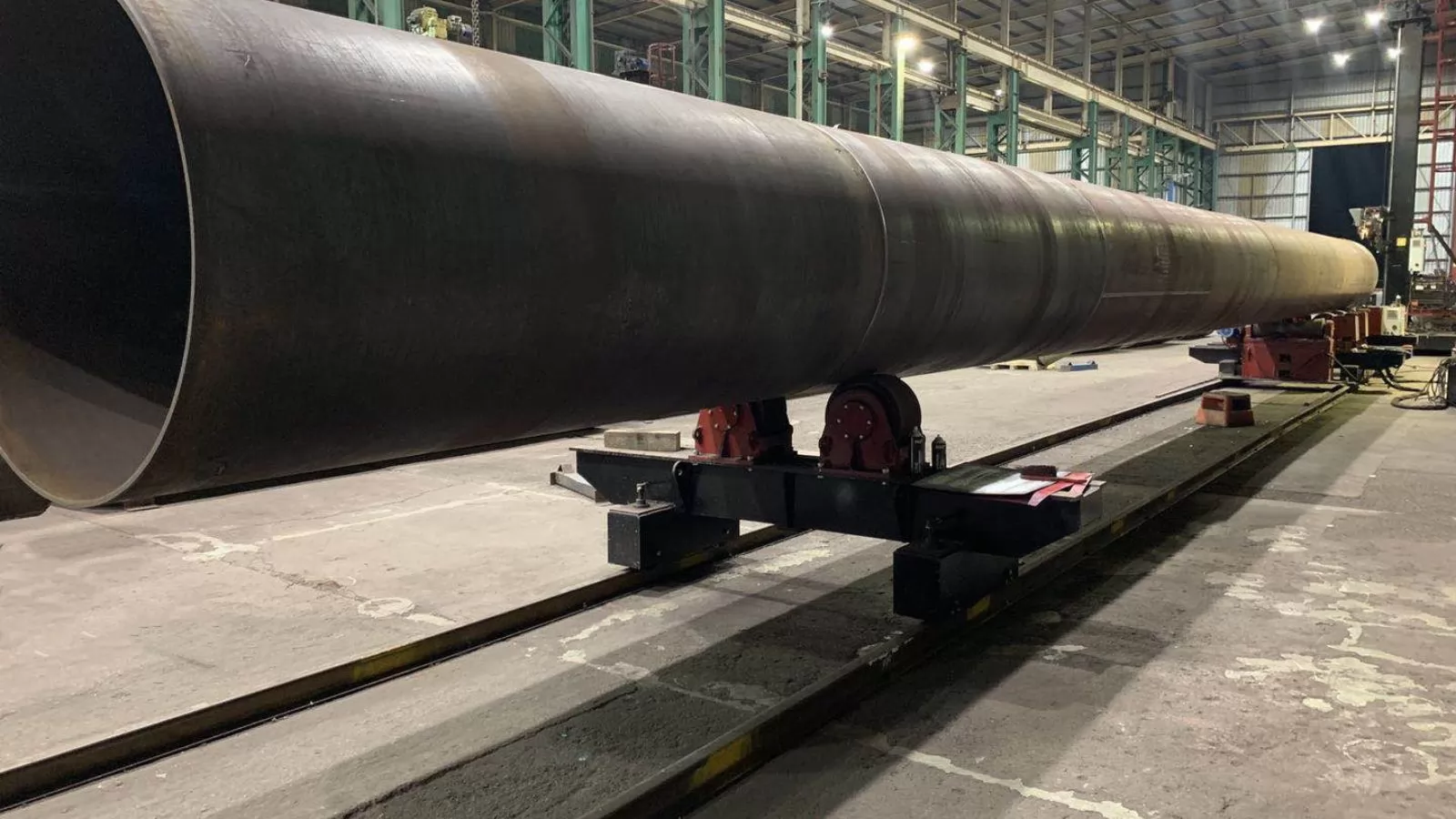


Welding turning rolls, also known as welding rotators or pipe turning rolls, are essential equipment in modern fabrication facilities. These specialized tools are designed to rotate cylindrical workpieces during welding operations, allowing welders to maintain optimal positions without the need to reposition themselves or the workpiece constantly.
At MISA Manufacturing, we understand that proper rotation of cylindrical vessels, pipes, and tanks is critical for achieving high-quality welds. Welding turning rolls serve as a pivotal component in the fabrication of numerous industrial products, from pressure vessels to large-diameter pipes, storage tanks, and other cylindrical structures.
The primary function of welding turning rolls is to provide controlled rotation of the workpiece. This rotation enables welders to work in the flat or horizontal position—the most efficient and effective welding position—throughout the entire circumference of the workpiece. The result is consistent weld quality, improved productivity, and enhanced worker safety.
Welding turning rolls play a crucial role in modern fabrication processes for several compelling reasons:
By enabling welders to maintain an optimal position throughout the welding process, turning rolls help ensure consistent penetration, uniform bead appearance, and reduced defects. The controlled rotation eliminates the need for awkward welding positions that might compromise quality.
With turning rolls, fabricators can significantly reduce the time spent repositioning workpieces. This continuous workflow minimizes downtime and can increase production rates by up to 40% compared to manual repositioning methods.
Manual handling of heavy cylindrical workpieces presents considerable safety risks. Turning rolls eliminate the need for workers to manually reposition heavy objects, substantially reducing the risk of injuries and creating a safer work environment.
While the initial investment in quality turning rolls may seem significant, the long-term cost benefits are substantial. Reduced labor requirements, minimized rework due to improved weld quality, and decreased project timelines all contribute to significant cost savings over time.
The strategic implementation of welding turning rolls in fabrication processes represents a fundamental shift from traditional manual welding approaches. Modern fabrication facilities consider these tools not as optional accessories but as essential equipment that forms the backbone of efficient cylindrical welding operations.
The market offers various configurations of welding turning rolls, each designed to address specific welding requirements and workpiece characteristics:
These versatile turning rolls feature polyurethane wheels mounted on self-aligning bearings. The design allows the rolls to automatically adjust to the workpiece diameter during rotation, making them ideal for handling variable-diameter vessels or tapered sections. Self-aligning rolls typically accommodate a broader range of workpiece diameters compared to conventional fixed-position rolls.
Conventional turning rolls consist of drive units (powered) and idler units (non-powered). The drive units contain motors and gear systems that provide the rotational force, while idler units offer additional support. These systems are configured in pairs or sets to accommodate the workpiece length and weight requirements. Conventional rolls are particularly well-suited for heavy-duty applications involving substantial workpiece weights.
These rolls feature manually or hydraulically adjustable positions to accommodate various workpiece diameters. The ability to adjust the distance between roll pairs provides versatility for fabrication shops that handle a wide range of workpiece sizes. Adjustable turning rolls often represent an excellent balance between versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Designed specifically for pipe welding operations, growing line turning rolls support longitudinal seam welding processes. These specialized rolls facilitate the creation of pipes from flat plate material by progressively forming and welding the cylindrical shape. They are essential in pipe manufacturing facilities and large-scale fabrication operations.
Various specialized turning roll configurations exist for unique applications, including:
At MISA Manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of turning roll solutions designed to meet diverse industry requirements and specifications. Our engineering team can help determine the most appropriate turning roll configuration based on your specific application needs.
Understanding the key components and design elements of welding turning rolls is essential for selecting the right equipment and ensuring optimal performance:
The drive system represents the heart of turning roll operations. Modern turning rolls typically utilize one of the following drive mechanisms:
Premium turning rolls like those offered by MISA incorporate inverter-controlled drive systems, allowing for precise speed adjustments and smooth acceleration/deceleration curves that protect workpieces from jerky movements.
The roller design significantly impacts turning roll performance and workpiece integrity:
The roller configuration determines the distribution of load and impacts stability during rotation. Advanced systems feature self-aligning roller designs that automatically adapt to workpiece variations.
Load capacity is determined by several design factors:
Proper matching of load capacity to application requirements is critical for both safety and performance. Under-specified turning rolls can lead to premature equipment failure and potential safety hazards.
Modern turning rolls incorporate increasingly sophisticated control systems:
Advanced control systems may include features such as programmable rotation sequences, synchronization between multiple roll sets, and integration with welding power sources for automated welding cycles.
Quality turning rolls incorporate various safety features:
These safety elements protect both operators and valuable workpieces from potential hazards during operation.
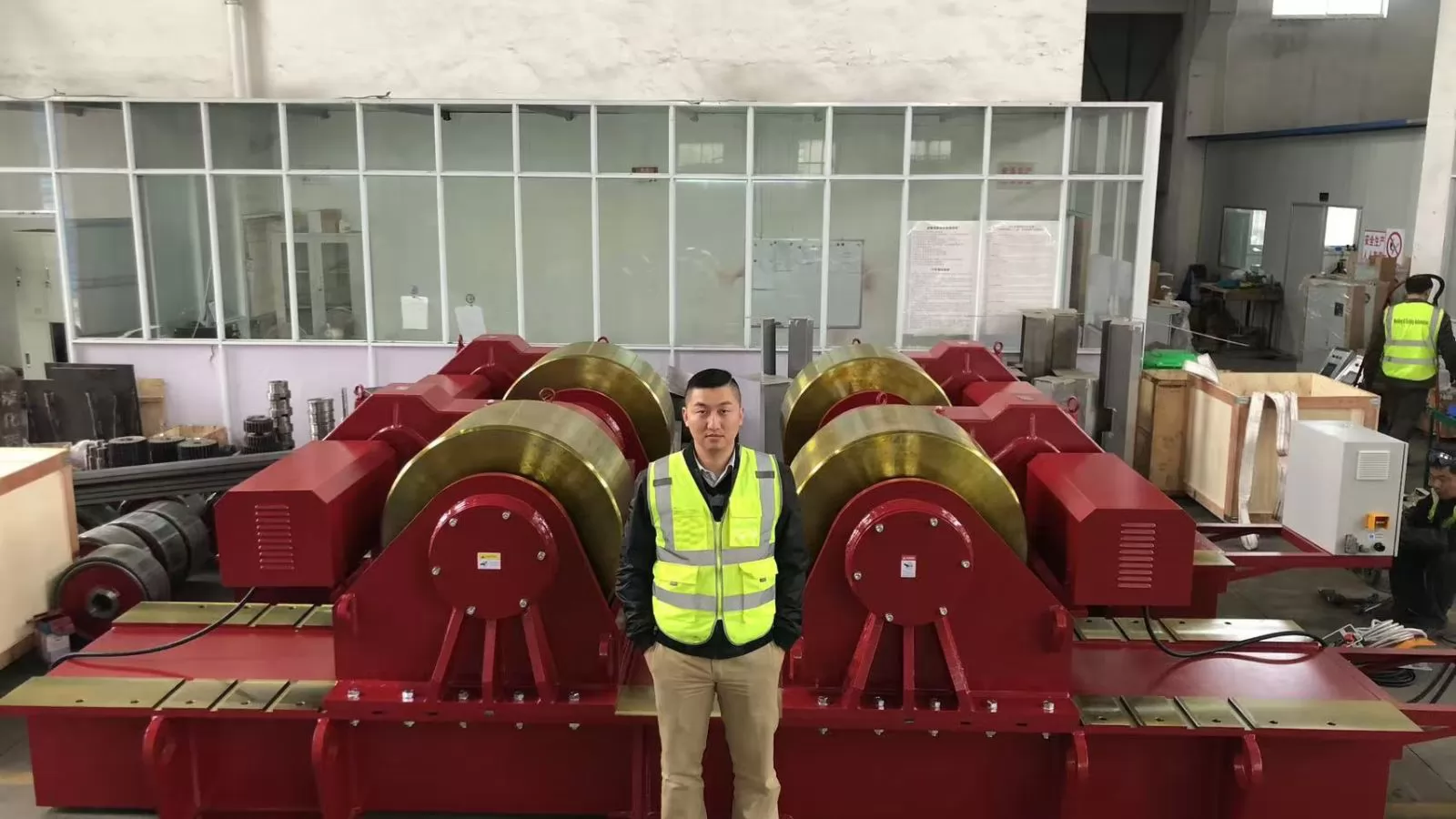

Selecting the appropriate welding turning rolls requires careful consideration of several key factors:
Begin by thoroughly analyzing your workpiece characteristics:
Always include a safety factor when calculating required capacity—typically a minimum of 25% above your maximum anticipated workpiece weight.
Assess your production needs and workflow considerations:
Evaluate the technical aspects that will impact performance and compatibility:
Balance initial investment against long-term considerations:
At MISA Manufacturing, our technical specialists can help you navigate these considerations and identify the turning roll solution that best matches your specific requirements. We offer comprehensive consultation services to ensure your equipment selection optimally addresses your fabrication challenges.
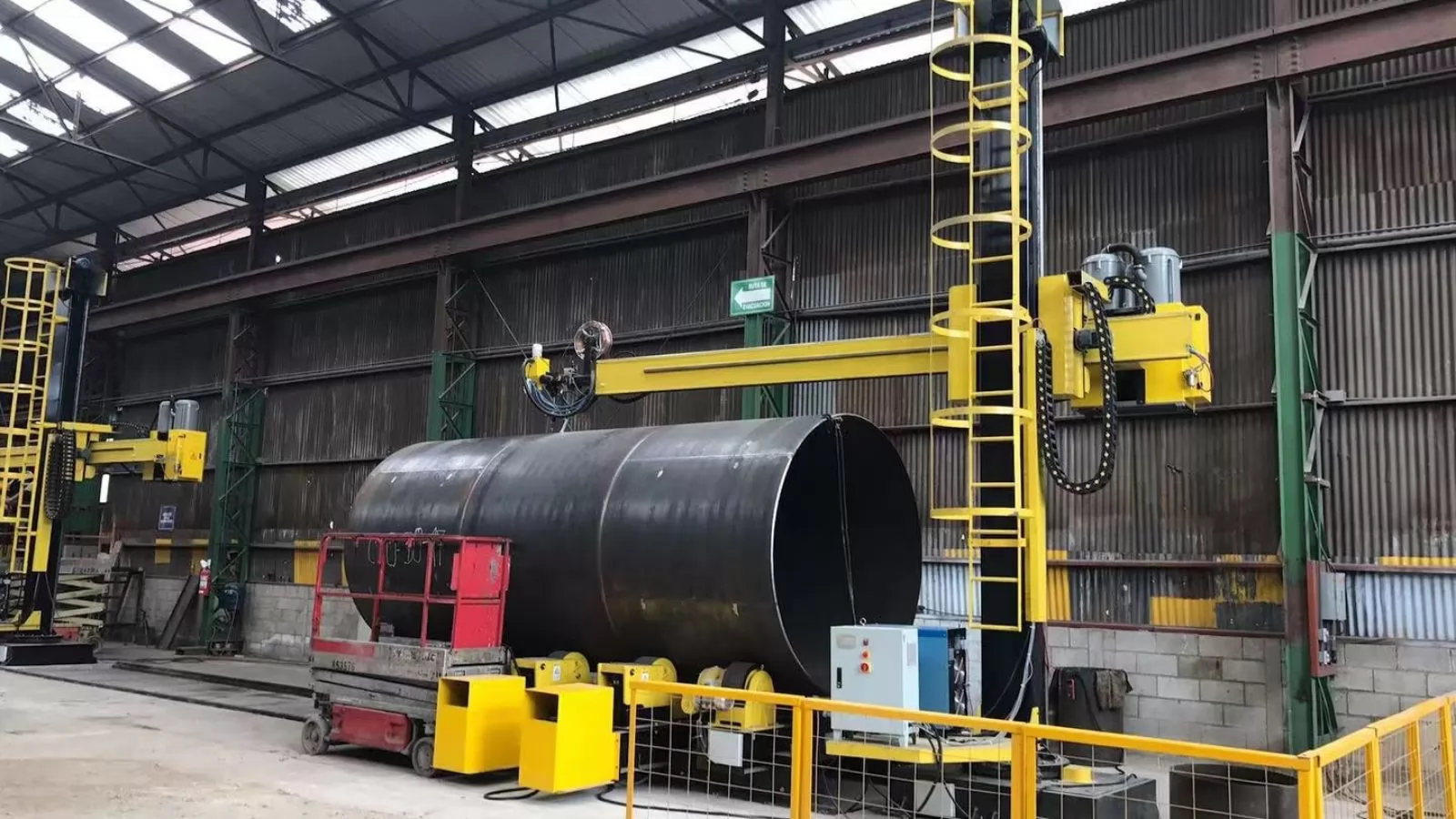

Proper setup and operation of welding turning rolls are critical for achieving optimal performance, ensuring safety, and extending equipment lifespan:
Follow these key steps when installing welding turning rolls:
Many fabricators find value in professional installation services, particularly for complex or high-capacity systems. At MISA, we offer comprehensive installation and commissioning services to ensure your equipment is properly set up from day one.
Proper workpiece loading techniques help prevent accidents and equipment damage:
Follow these operational guidelines to maximize efficiency and safety:
Comprehensive operator training is essential for safe and efficient operation:
MISA offers comprehensive operator training programs tailored to your specific equipment and application requirements, ensuring your team can maximize the value of your turning roll investment.
Implementing a structured maintenance program for your welding turning rolls is essential for ensuring reliable operation, maximizing equipment lifespan, and preventing costly downtime:
Establish scheduled inspection protocols:
Maintaining detailed inspection records helps identify developing issues before they lead to equipment failure or safety concerns.
Proper lubrication is critical for turning roll longevity:
The drive system requires specific maintenance attention:
Rollers represent a critical wear component:
Implement a comprehensive preventive maintenance program:
| Component | Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Bearings | Lubrication, inspection for wear | Monthly |
| Drive Components | Tension check, lubrication, alignment | Quarterly |
| Electrical Systems | Connection verification, component testing | Semi-annually |
| Rollers | Surface inspection, cleaning, rotation | Weekly |
| Control Systems | Calibration, function testing | Quarterly |
| Structural Components | Inspection for cracks, deformation | Semi-annually |
MISA provides comprehensive maintenance documentation with all turning roll systems and offers service contracts that include scheduled maintenance visits by certified technicians. Our preventive maintenance programs are designed to maximize equipment reliability and minimize unplanned downtime.
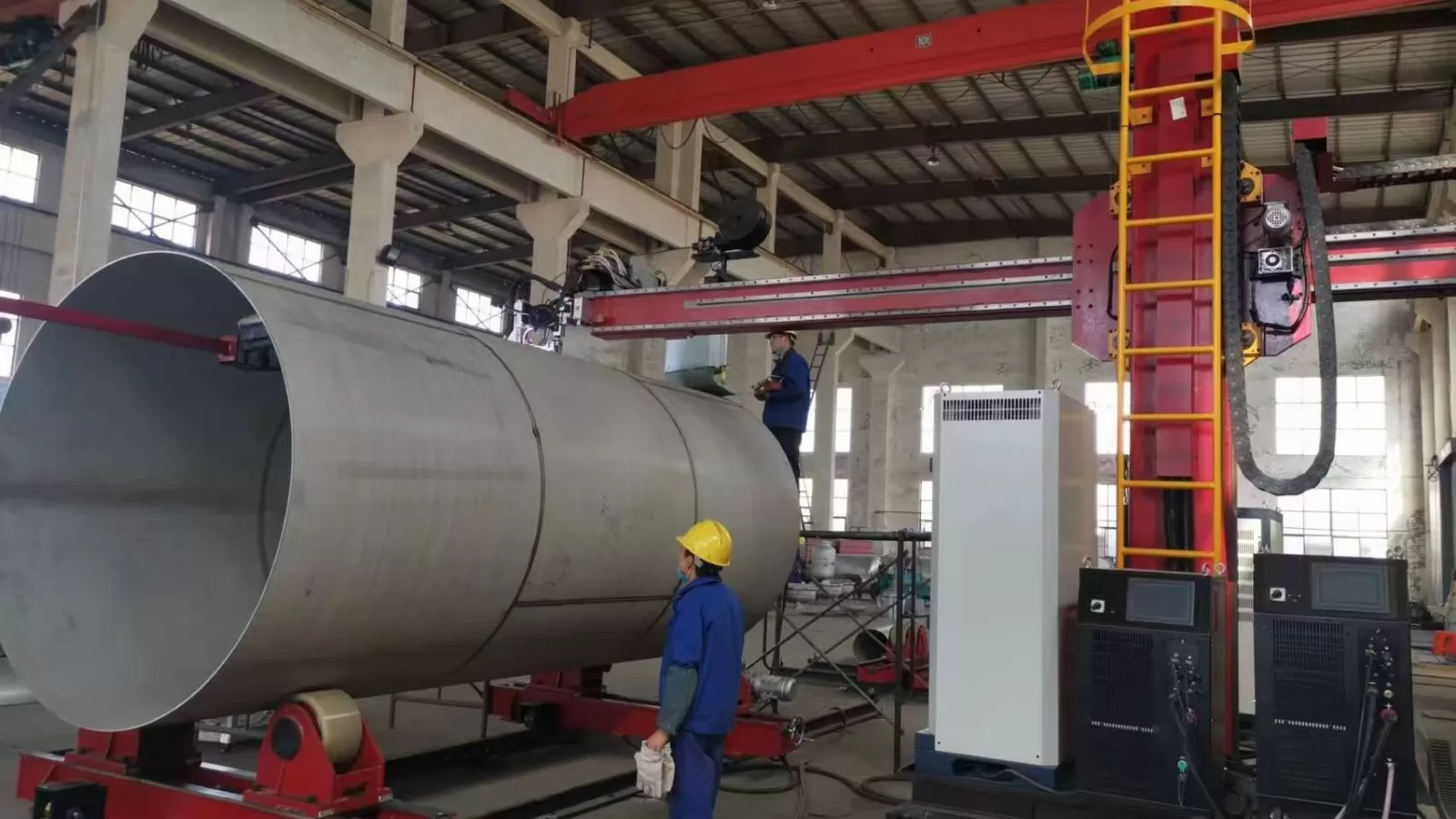

Prioritizing safety when operating welding turning rolls is essential for protecting personnel and preventing accidents. Implement these comprehensive safety measures:
Follow these operational safety guidelines:
Verify that your turning rolls include these essential safety features:
Require appropriate PPE for all personnel working with or near turning rolls:
Maintain a safe working environment:
Establish clear emergency protocols:
At MISA, safety is our highest priority. Our turning roll systems are designed with comprehensive safety features, and we provide detailed safety documentation and training resources with all equipment. We recommend regular safety audits and continuous reinforcement of safety protocols for all turning roll operations.
Welding turning rolls serve diverse industries and applications, demonstrating their versatility and critical role in modern fabrication:
Turning rolls are indispensable in pressure vessel fabrication, where high-quality circumferential welds are essential for integrity and safety. Manufacturers utilize turning rolls to:
Pressure vessel codes such as ASME Section VIII require stringent weld quality, making proper rotation equipment crucial for meeting certification requirements.
In pipeline manufacturing and field fabrication, turning rolls support:
Modern pipeline projects rely heavily on turning roll technology to meet increasingly demanding quality and productivity requirements.
Storage tank manufacturers utilize turning rolls for:
The large diameters and substantial weights involved in storage tank fabrication make specialized turning roll systems particularly valuable.
The renewable energy sector relies on turning rolls for wind tower production:
With increasing wind tower sizes in modern installations, high-capacity turning rolls have become essential for efficient production.
Maritime fabrication utilizes turning rolls for:
The demanding standards of maritime construction make high-precision turning roll systems invaluable for achieving required quality levels.
Power industry applications include:
The critical nature of power generation equipment demands the precision and quality enabled by proper turning roll systems.
At MISA Manufacturing, our turning roll systems serve clients across these diverse industries. Our engineering team works closely with customers to develop application-specific solutions that address unique challenges and requirements in each sector.
Welding turning rolls represent a critical component in modern fabrication processes, delivering substantial benefits in terms of weld quality, productivity, safety, and cost-effectiveness. As we've explored throughout this comprehensive guide, these seemingly simple rotation devices embody sophisticated engineering principles and continue to evolve with advancing technology.
The selection of appropriate turning rolls requires careful consideration of workpiece characteristics, production requirements, technical factors, and economic considerations. By thoroughly evaluating these elements, fabricators can identify turning roll solutions that precisely match their operational needs and deliver optimal value.
Proper setup, operation, and maintenance of turning rolls are essential for maximizing their performance and lifespan. By implementing structured maintenance programs and adhering to operational best practices, fabrication facilities can ensure reliable operation and prevent costly downtime.
Safety considerations must remain paramount in all turning roll operations. Comprehensive safety protocols, appropriate equipment features, and thorough operator training are non-negotiable elements of responsible turning roll implementation.
As technology continues to advance, welding turning rolls are evolving from purely mechanical devices into intelligent, connected components within modern smart factories. These advancements offer exciting opportunities for enhanced productivity, quality, and efficiency in fabrication operations.
At MISA Manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of welding turning rolls designed to meet the diverse needs of modern fabrication facilities. Our engineering team provides personalized consultation to ensure you select the optimal solution for your specific applications.
Contact our technical specialists today to discuss your turning roll requirements and discover how MISA's innovative solutions can enhance your fabrication capabilities.
Contact MISA Today