.png)
.png)
.png)


Welding positioners play a critical role in modern manufacturing by precisely holding, rotating, and tilting workpieces to optimize welding operations. They help improve weld quality, enhance safety, and increase overall productivity. Understanding the different types of welding positioners is essential for selecting the right equipment and achieving consistent results in welding processes.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to various welding positioner types, their features, applications, and selection criteria, helping you make informed decisions for your welding needs.
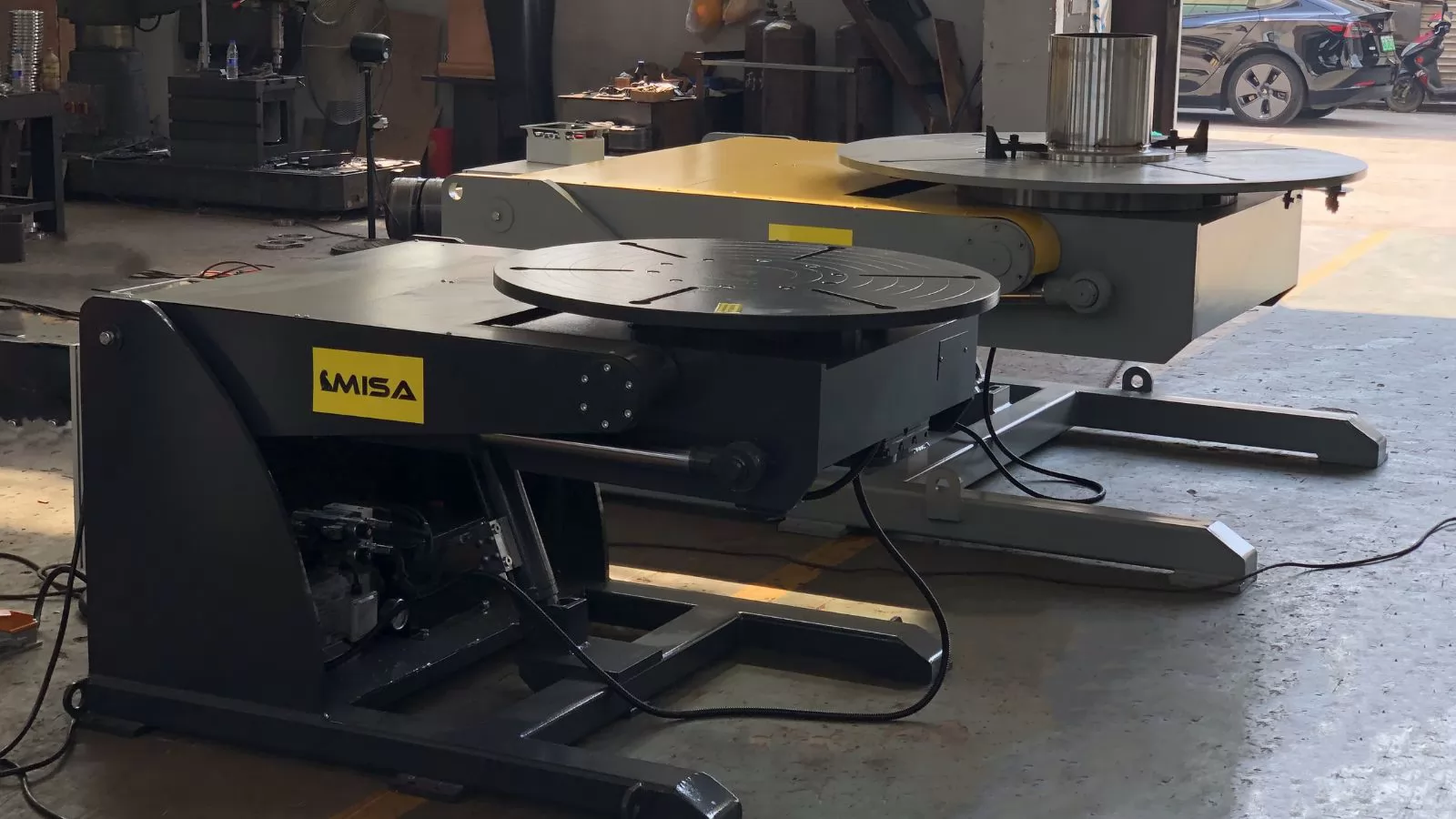

A welding positioner is a mechanical device designed to hold, rotate, and tilt workpieces to provide optimal access for welding. By positioning the workpiece correctly, it allows welders to maintain consistent angles, reduce fatigue, and achieve higher-quality welds.
Welding positioners come in various designs and configurations, offering benefits such as:
Welding positioners can be classified based on several criteria, including movement axes, workpiece type, and control method. Understanding these classifications helps in selecting the right positioner for specific welding applications.
Selecting the right welding positioner is essential to achieving high-quality welds, maximizing productivity, and ensuring operator safety. The ideal solution depends on several technical and operational factors that should be evaluated before making a purchase.
The dimensions and weight of the workpiece are the primary considerations. Positioners must be rated to safely handle the maximum load while maintaining stability during rotation and tilting. Irregular or asymmetrical parts may require multi-axis or custom-built positioners.
Simple welding applications may only require a 2-axis positioner, while more complex geometries benefit from 3-axis, skyhook, or robotic positioners. Understanding the required range of motion helps prevent over-specification or underperformance.
For low-volume or manual welding operations, manual or motorized positioners may be sufficient. High-volume production environments often benefit from automated or robotic welding positioners that offer higher consistency and reduced cycle times.
Consider whether the positioner needs to integrate with robotic welding cells, PLC controls, or existing production lines. Floor space, operator accessibility, and ergonomics should also be evaluated to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Based on different welding applications and production requirements, MISA offers a wide range of welding positioners designed for precision, durability, and efficiency.
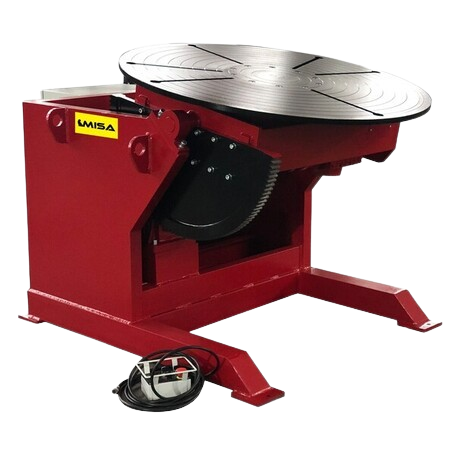

Ideal for standard welding applications requiring rotation and tilt. Suitable for small to medium-sized workpieces.
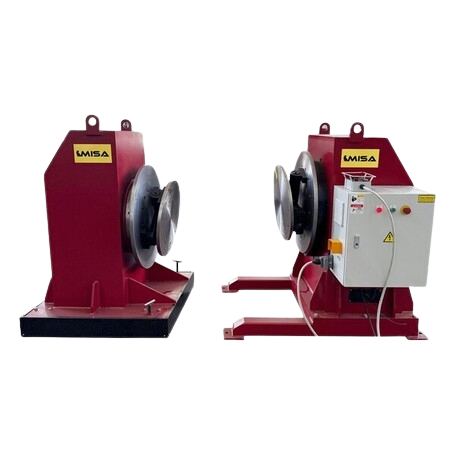

Designed for long and heavy components, offering stable rotation and consistent weld quality.
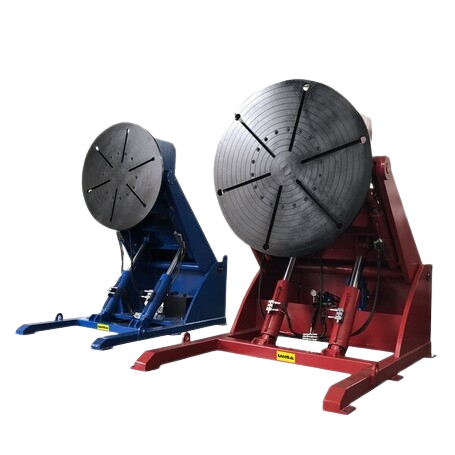

Optimized for automated welding lines, providing high precision and seamless robot integration.
Welding positioners are widely used across multiple industries to improve weld quality, enhance productivity, and ensure operator safety. Different industries often require specific types of welding positioners based on workpiece geometry, weight, and production volume.
In the automotive industry, welding positioners are commonly used for chassis components, frames, exhaust systems, and subassemblies. Turntable positioners, 2-axis positioners, and robotic welding positioners are widely adopted to support high-volume, repetitive welding tasks while maintaining consistent weld quality.
Manufacturers of heavy equipment and construction machinery rely on hydraulic and headstock-tailstock welding positioners to handle large, heavy, and irregular workpieces. These positioners provide high load capacity and stable rotation, enabling precise welding of structural components.
Pipe welding positioners, roller bed positioners, and specialized elbow or ring-type positioners are essential in pipeline and pressure vessel fabrication. These systems ensure uniform weld penetration and consistent rotation, reducing the risk of weld defects.
Aerospace and precision manufacturing applications demand exceptional accuracy and repeatability. Multi-axis welding positioners, including 3-axis and skyhook positioners, are commonly used to weld complex geometries and critical components with tight tolerances.
In general fabrication workshops, manual and motorized welding positioners are widely used for a broad range of custom and low-to-medium volume projects. Portable welding positioners offer flexibility and efficiency for diverse fabrication needs.
The main types of welding positioners include 2-axis positioners, 3-axis positioners, turntable positioners, pipe welding positioners, headstock-tailstock positioners, and robotic welding positioners. Each type is designed to support different workpiece geometries, weights, and production requirements.
A turntable positioner primarily provides horizontal rotation and is ideal for simple or flat workpieces. A 3-axis welding positioner offers rotation, tilt, and vertical lift, making it suitable for more complex welding applications that require greater flexibility and precision.
Welding positioners allow welders to maintain optimal welding angles and consistent travel speeds. By reducing manual repositioning and operator fatigue, positioners help produce more uniform welds and reduce the likelihood of defects.
Yes, many welding positioners are designed to integrate seamlessly with robotic welding systems and PLC controls. Robotic welding positioners are commonly used in automated production lines to improve efficiency, repeatability, and throughput.
Choosing the right welding positioner depends on factors such as workpiece size, weight, shape, required movement, production volume, and automation needs. Consulting with an experienced manufacturer like MISA can help ensure the optimal solution for your specific application.
Understanding the different types of welding positioners is essential for improving weld quality, enhancing workplace safety, and increasing production efficiency. From basic 2-axis positioners to advanced robotic and custom-built solutions, each type serves a specific purpose based on application requirements.
As an experienced welding positioner manufacturer, MISA provides a comprehensive range of standard and customized welding positioners designed to meet the demands of diverse industries. By selecting the right welding positioner and working with a trusted supplier, manufacturers can achieve consistent, high-quality welding results and long-term operational success.
If you are evaluating welding positioner options for your production line or automation project, MISA’s engineering team is ready to support your needs with expert guidance and tailored solutions.