.png)
.png)
.png)


Pipe welding is a fundamental process in industries such as oil and gas, shipbuilding, power generation, and manufacturing. The quality of a pipe weld determines the overall reliability and safety of the entire system. Choosing the right welding type not only affects production efficiency but also long-term maintenance and operational costs.
To overcome these challenges, many manufacturers are embracing automation. Automated pipe welding solutions ensure consistency, speed, and safety—while reducing operator dependence.
As a leading manufacturer of pipe welding automation equipment, MISA offers high-performance welding rotators, positioners, and fit-up rollers that optimize welding angles, maintain alignment, and enhance weld quality across all pipe sizes and materials.
In the following sections, we’ll explore the main types of pipe welding, their applications, and how MISA’s advanced systems can help you achieve better results with greater efficiency.
Pipe welding can be performed using several different methods, each suited for specific materials, production requirements, and performance goals. Below are the five most commonly used types of pipe welding and how they apply to industrial operations.
Also known as “stick welding,” SMAW is one of the oldest and most versatile welding methods. It uses a flux-coated electrode to create an electric arc between the electrode and the pipe surface. This method is ideal for outdoor or on-site repair work, as it can handle a wide range of materials and conditions.
When consistency and precise positioning are required, MISA’s welding positioners help operators control the work angle and improve accessibility during SMAW processes, especially for large or awkward pipe assemblies.
TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce high-quality, precise welds. It is widely used in industries that require clean and defect-free joints, such as chemical processing and aerospace. However, the process can be slow and requires skilled operators.
To achieve consistent TIG welds on cylindrical workpieces, MISA’s welding rotators maintain stable and adjustable rotation, ensuring smooth, uniform weld seams and reducing operator fatigue.
MIG welding uses a continuously fed wire electrode and shielding gas to create fast, efficient welds. It is highly productive and commonly used in manufacturing environments where speed and repeatability are crucial. MIG welding can be easily automated, making it compatible with modern production lines.
By integrating MISA’s fit-up rotators into MIG welding systems, operators can align and join pipes seamlessly before welding, improving joint precision and minimizing rework.
FCAW is similar to MIG welding but uses a tubular wire filled with flux, allowing for better penetration and higher deposition rates. It performs well in outdoor conditions and is widely applied in construction, shipbuilding, and heavy fabrication.
When working on large, heavy-duty pipe sections, MISA’s self-aligning rotators support and rotate the pipes smoothly, enabling consistent weld quality even on demanding FCAW applications.
SAW involves forming an arc beneath a layer of granular flux, which shields the molten metal from contamination and allows deep penetration. It’s commonly used for large-diameter pipes, tanks, and pressure vessels. This process is highly productive and almost always mechanized or automated.
For SAW applications, MISA’s heavy-duty welding positioners provide stable support and rotation, ensuring even weld distribution and precise control of large, heavy pipes during automated operations.
Even with advanced welding techniques, pipe fabrication projects often face a range of technical and operational challenges. These issues can affect weld quality, consistency, and overall productivity. Understanding these challenges is key to identifying the right welding solutions and automation tools.
One of the most frequent problems in pipe welding is maintaining consistent alignment between pipe sections. Even slight misalignments can result in incomplete fusion, undercuts, or porosity. Manual alignment is time-consuming and heavily dependent on operator experience.
With MISA’s fit-up rotators, fabricators can precisely position and align pipes before welding, reducing setup time and ensuring accurate joint preparation.
Manual pipe welding requires sustained concentration and physical endurance, especially when working on large or thick-walled pipes. Fatigue can lead to irregular torch angles, unstable travel speeds, and inconsistent bead profiles—all of which affect weld quality.
By integrating MISA’s welding rotators and positioners, operators can work more comfortably and consistently, reducing the risk of human error while improving overall efficiency.
Maintaining a stable welding speed is crucial for achieving uniform penetration and avoiding defects such as burn-through or incomplete fusion. Manual handling often leads to fluctuations in heat input and bead size, especially when rotating pipes by hand.
Automated rotation systems like MISA’s precision-controlled rotators ensure smooth, consistent pipe rotation throughout the welding cycle, resulting in higher quality welds and reduced rework.
As industries face a growing shortage of skilled welders, relying solely on manual welding becomes less sustainable. Labor-intensive setups and repetitive tasks increase operational costs and limit scalability.
With automated systems such as MISA’s welding positioners, manufacturers can reduce manual handling, shorten cycle times, and maintain high throughput with fewer operators.
Ensuring consistent weld quality across multiple joints and production runs is a challenge even for experienced welders. Variations in pipe diameter, material composition, or heat input can all lead to uneven welds or defects.
By using MISA’s integrated pipe welding automation systems, manufacturers can maintain repeatable, high-quality welds while minimizing inspection failures and material waste.
Addressing these common challenges requires more than just skilled labor—it demands precise equipment and intelligent automation. That’s where MISA’s advanced welding solutions truly make a difference.
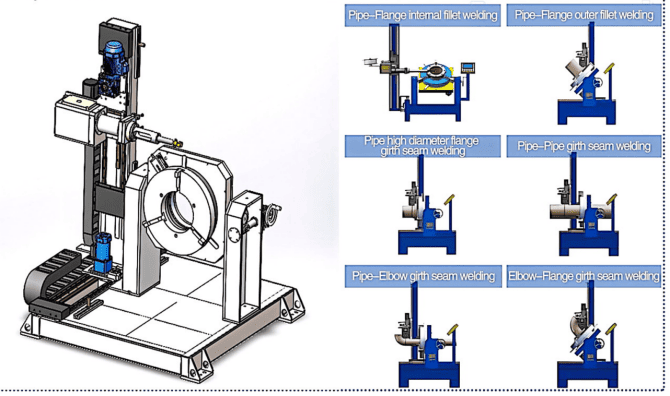
MISA provides a complete range of pipe welding automation equipment designed to enhance accuracy, productivity, and safety across all industrial applications. Each system is engineered to address the most common issues faced during pipe welding — from alignment to positioning and rotation control.
| Challenge | MISA Solution | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inconsistent pipe alignment | Fit-up Rotators | Accurately aligns pipe sections and minimizes setup time before welding. |
| Operator fatigue and human error | Welding Rotators | Supports and rotates pipes automatically, ensuring smooth and consistent welds. |
| Unstable welding speed and penetration | Variable-Speed Rotators | Ensures steady rotation and heat input, improving bead uniformity and weld penetration. |
| Limited skilled labor and high costs | Welding Positioners | Reduces manual handling by automatically adjusting the workpiece to optimal angles. |
| Quality inconsistency and rework | Integrated Welding Automation Systems | Ensures repeatable, high-quality welds with precise control of speed and position. |
By integrating MISA’s advanced welding solutions, manufacturers can significantly improve weld quality, reduce rework, and achieve higher productivity with minimal operator intervention. These technologies are already trusted across industries like oil & gas, petrochemical, and structural fabrication.
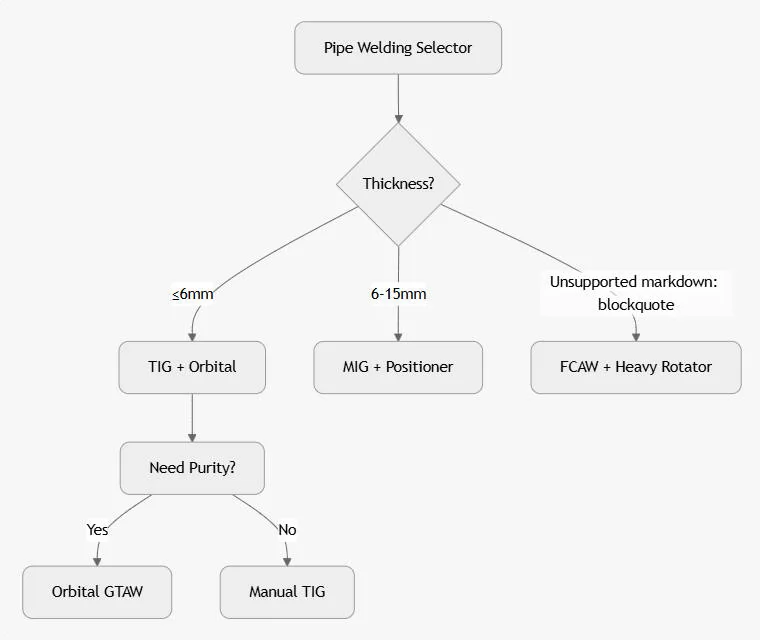
Selecting the right welding method is only one part of the process — the quality and efficiency of the operation also depend on the equipment used to handle, position, and rotate pipes. That’s where MISA comes in.
| Welding Type | Recommended MISA Equipment | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| MIG/GMAW Welding | Welding Rotators | Provides steady rotation for consistent bead formation and reduced defects. |
| TIG/GTAW Welding | Welding Positioners | Offers precise angle control for thin-walled and high-spec pipes. |
| SAW (Submerged Arc Welding) | Self-Aligning Rotators | Automatically adapts to pipe diameters, ideal for long-run and heavy-duty applications. |
| Manual SMAW Welding | Fit-Up Rotators | Simplifies alignment and joint preparation before manual welding. |
If you’re planning to enhance your pipe welding efficiency, explore MISA’s full range of solutions at www.misamfg.com or contact their team for a custom consultation.
Pipe welding is an essential process across industries such as oil & gas, power generation, shipbuilding, and infrastructure. Understanding the different types of pipe welding—and matching them with the right automation tools—ensures both production efficiency and long-term reliability.
Each method—from TIG and MIG to SAW and orbital welding—offers unique benefits for specific materials and project scales. However, to truly maximize weld precision, safety, and consistency, it’s crucial to pair your welding process with advanced handling and positioning equipment.
That’s where MISA delivers value. With a proven range of welding rotators, positioners, and fit-up rollers, MISA enables manufacturers worldwide to achieve perfect alignment, stable rotation, and superior weld quality—no matter the project size or complexity.
If you’re ready to upgrade your welding efficiency and reduce manual errors, visit MISA Manufacturing to explore a customized automation solution built around your production needs.
The main types include MIG/GMAW, TIG/GTAW, Stick/SMAW, Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), and Orbital Welding. Each has unique advantages depending on pipe thickness, material, and project requirements.
TIG (GTAW) welding is preferred for stainless steel pipes because it provides precise control, clean welds, and minimal contamination—ideal for industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical plants.
Automation is key. Using welding rotators and positioners allows for consistent pipe rotation and stable welding angles, significantly increasing productivity and weld consistency while reducing operator fatigue.
MISA provides high-performance welding automation systems—including rotators, positioners, and fit-up rollers—that support all major welding types. These machines maintain precise alignment, stabilize rotation, and allow seamless integration with MIG, TIG, and SAW setups. The result is faster throughput, higher accuracy, and lower production costs for fabricators worldwide.
You can explore MISA’s full product line and request a custom quote directly on their official website: https://www.misamfg.com/.